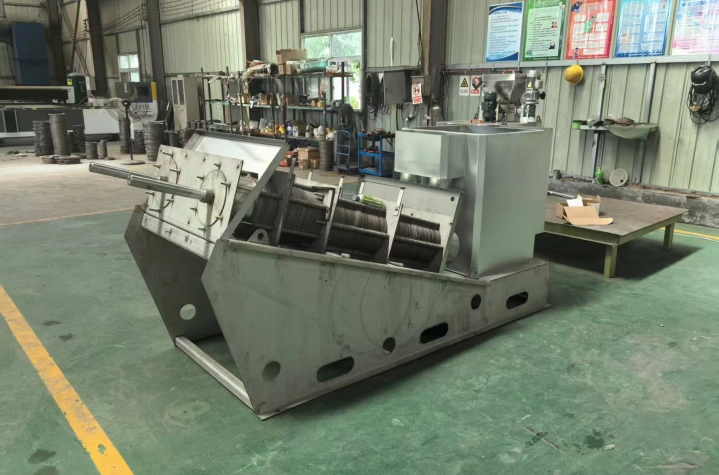
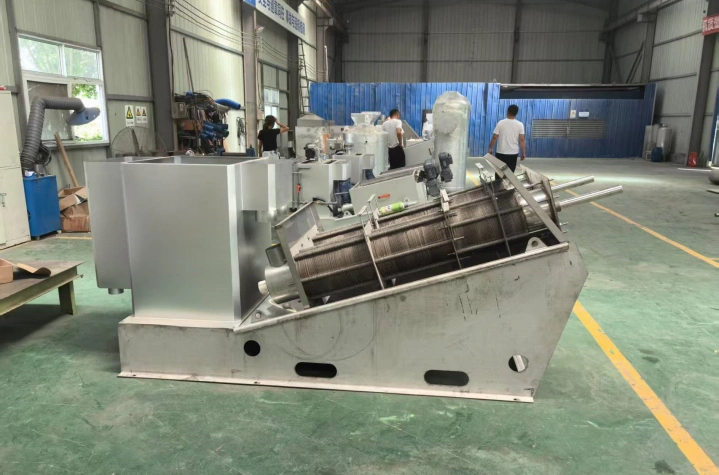
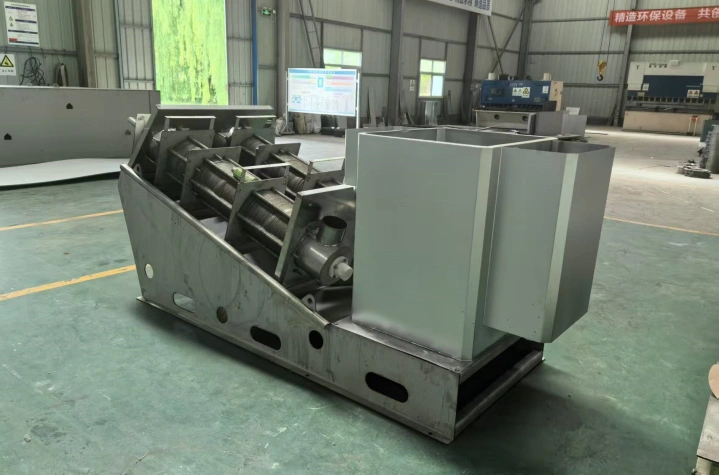
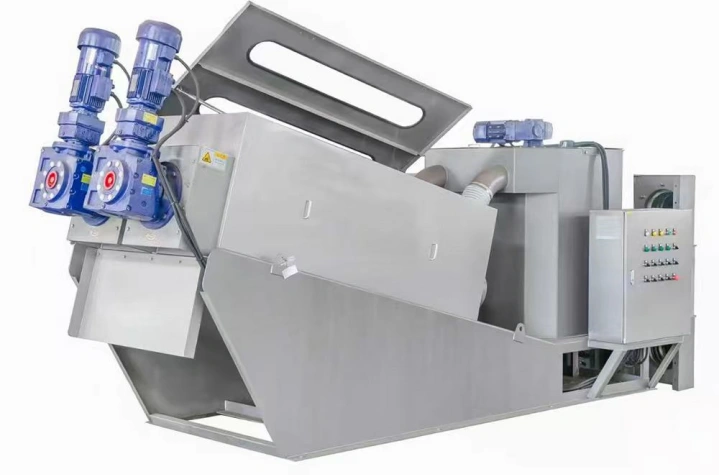
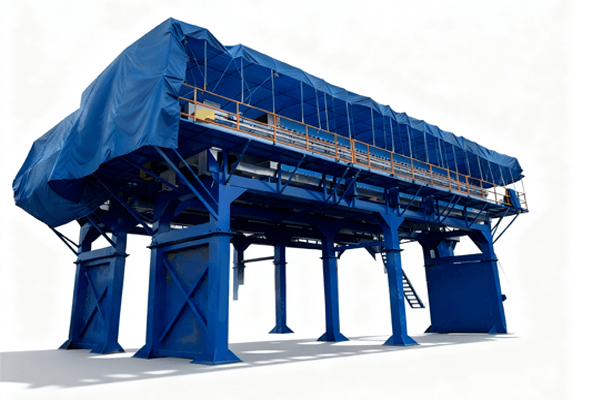
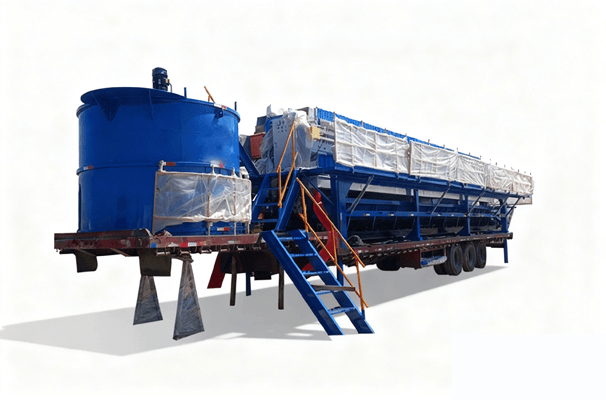
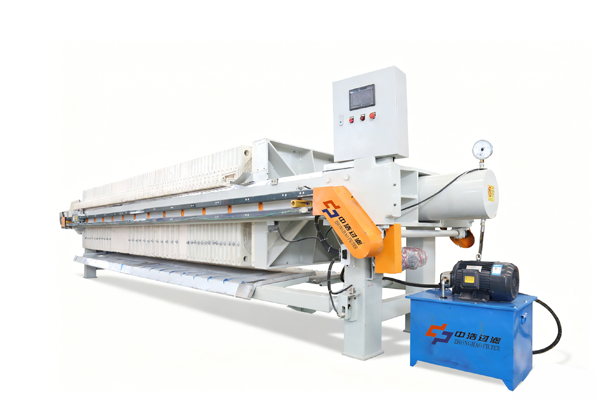
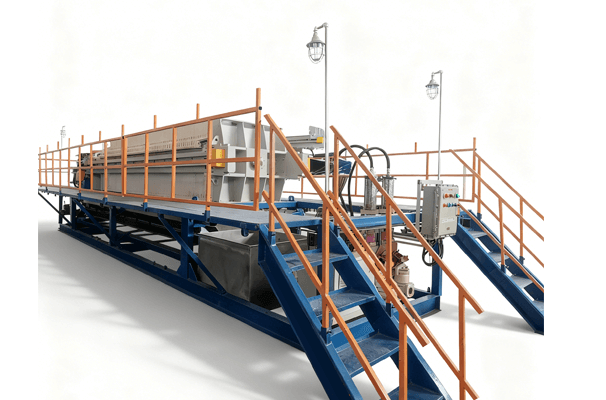
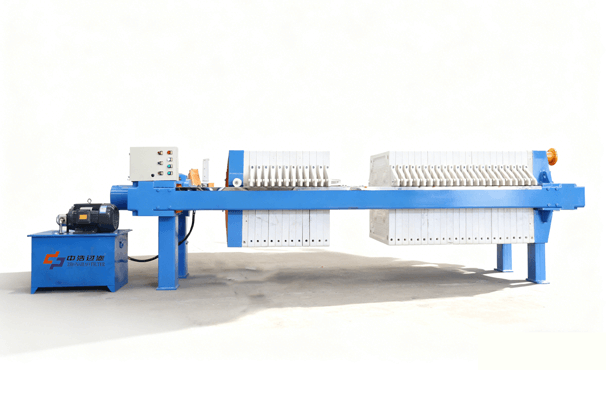
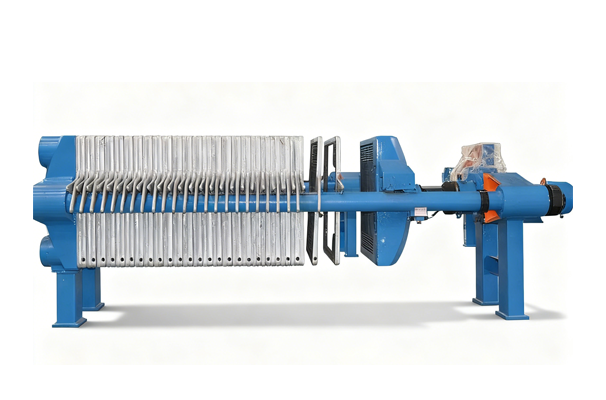
Product Introduction
Its core structure comprises a concentration section and a dewatering section. The spiral pushes the sludge, gradually compressing it. The filtrate is discharged through the gaps between the rings, ultimately forming a low-moisture sludge cake. The device operates stably, requiring no filter cloth or centrifugal device, making it suitable for continuous, automated operations.
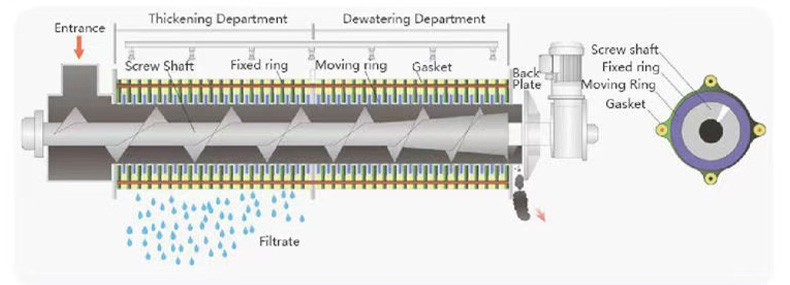
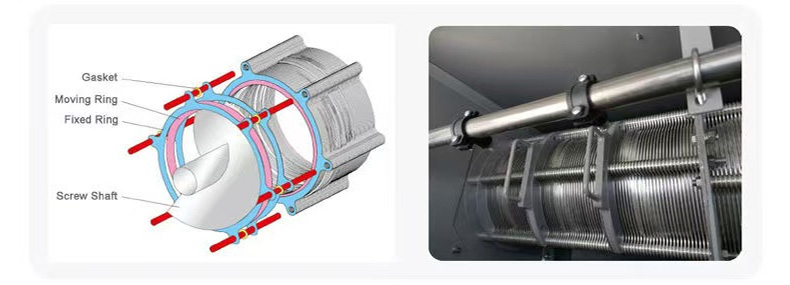
Key Features and Advantages
The low-speed screw shaft (2-4 rpm) consumes only one-third of the power of traditional equipment, reducing sludge moisture content from 99% to below 80%, significantly reducing sludge volume.
The self-cleaning filter slot design eliminates the need for frequent flushing and saves up to 70% water.
The integrated electronic control system supports 24/7 unattended operation.
Simple operation requires only regular lubrication and component inspection, reducing maintenance costs by 50%.
The modular stainless steel construction means only the screw shaft and the running ring require replacement, resulting in a lifespan of over five years.
Main Applications
Dewatering activated sludge from sewage treatment plants to reduce transportation and landfill costs.
Treatment of high-difficulty wastewater from the chemical, pharmaceutical, food (including grease sludge), printing and dyeing industries.
Separation of viscous materials such as heavy metal-containing electroplating sludge, aquaculture wastewater, and restaurant waste.
Parameter Information
| Model | DS Standard Capacity (kgds/h) | Sludge Treatment Capacity (m³/h) | |||||
| Low Concentration | High Concentration | 10000mg/L | 20000mg/L | 30000mg/L | 40000mg/L | 50000mg/L | |
| RDL101 | 3 | 5 | ~0.3 | -0.15 | ~0.13 | -0.12 | ~0.1 |
| RDL131 | 6 | 12 | ~0.6 | ~0.3 | ~0.28 | -0.26 | ~0.24 |
| RDL201 | 10 | 20 | ~1.0 | -0.5 | ~0.46 | ~0.43 | ~0.4 |
| RDL202 | 20 | 40 | ~2.0 | ~1.0 | ~0.92 | ~0.86 | ~0.8 |
| RDL251 | 15 | 30 | -1.5 | -0.75 | -0.7 | -0.65 | ~0.6 |
| RDL252 | 30 | 60 | ~3.0 | ~1.5 | ~1.4 | ~1.3 | ~1.2 |
| RDL301 | 40 | 70 | -4.0 | -2.0 | ~1.8 | ~1.6 | ~1.4 |
| RDL302 | 80 | 140 | ~8.0 | ~4.0 | ~3.6 | ~3.2 | ~2.8 |
| RDL303 | 120 | 210 | -12 | -6.0 | -5.4 | ~4.8 | ~4.2 |
| RDL351 | 70 | 120 | ~7 | ~3.5 | ~3.2 | ~3.0 | ~2.4 |
| RDL352 | 140 | 240 | ~14 | ~7.0 | ~6.4 | ~6.0 | ~4.8 |
| RDL353 | 210 | 360 | ~21 | ~10.5 | ~9.6 | ~9.0 | ~7.2 |
| RDL401 | 110 | 160 | ~11 | ~5.5 | ~4.5 | ~4.0 | ~3.2 |
| RDL402 | 220 | 320 | ~22 | ~11 | ~9.0 | ~8.0 | ~6.4 |
| RDL403 | 330 | 480 | ~33 | ~16.5 | ~13.5 | ~12.0 | ~9.6 |
| RDL404 | 440 | 640 | ~44 | ~22 | ~18 | ~16.0 | ~12.8 |